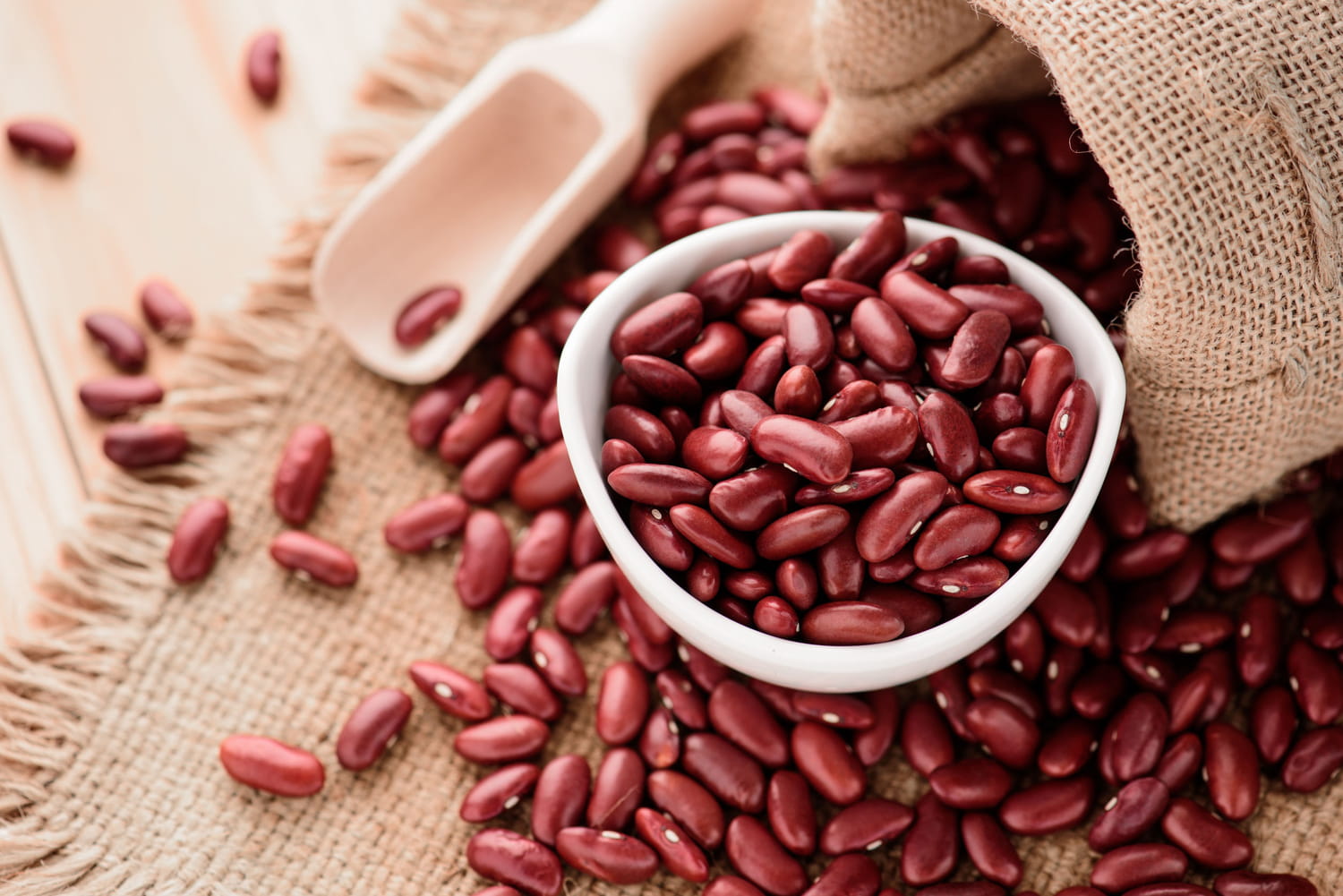
Red bean, like many of its fellows among legumes, has a bad press. And it’s a shame! Tour of his benefits and advice to savor it without risk with dietician Catherine Conan.
Red bean is a legume In the same way as lenses even if its starch content suggests that it is a starchy. It is one of the pulses.
- Red bean has diuretic virtues by the presence of potassium and its sodium poverty,
- It benefits from an average glycemic index which allows better stability of diabetes without forgetting a decrease in cardiovascular risk (presence of phytosterols).
- Its antioxidants, in particular anthocyanins, protect the organism against the action of free radicals (toxic molecules).
- His dietary fibers give it a full effect and improve intestinal functioning.
- It hardly contains lipids.
- It has a particularly interesting content of calcium, iron and vitamins of group B, in particular vitamin B9 (antioxidant vitamin).
On the clock 115 calories 100 g. Barely more than potatoes.
Red bean is a very appreciable source of vegetable protein despite the absence of certain sulfur amino acids. To overcome this insufficiency, it is enough to associate them with other vegetable proteins such as those of cereals or those of animal proteins, prerogative of meat, fish, eggs, dairy products … It’s up to you to improvise for a winning combination!
| Nutrients | Cooked red bean: content for 100 g | Legumes: average food |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 9.63 g | 1.7 g |
| Carbohydrates | 12.1 g | 4.4 g |
| – including sugars | 0.56 g | 2.3 g |
| – including starch | 11.5 g | 0.9 g |
| Dietary fiber | 11.6 g | 2 g |
| Lipids | 0.6 g | 0.6 g |
| – including cholesterol | 0.0 mg | 0.2 mg |
| – including saturated fatty acids | 0.19 g | 0.1 g |
| – including monounsaturated fatty acids | 0.16 g | 0.2 g |
| – including polyunsaturated fatty acids | 0.24 g | 0.1 g |
| Water | 65 g | 90 g |
Do you follow a hypocaloric diet? No worries, red bean is a very good source of carbohydrates therefore of energy. It is full so do not deprive yourself, you will crack less on other foods.
Red bean contains many antinutritional factors but with a soaking And a change of cooking water, the effects are minimized. Some oligosaccharides that make up the red bean are responsible for flatulencewhich has the effect of slowing down its consumption.
In addition, the presence of phytic acid limits the absorption of calcium and other minerals but occasional consumption is not detrimental. Finally, in people with colon pathologies, the consumption of red beans is not recommended.